Heredity AND Evaluation
Heredity AND Evaluation
Heredity: - It is the genetic makeup of a particular organism which passes into successive generation .Theses are the characters of parent’s passes into their off springs.
Variation: - These are the physiological, structural or genetic changes occurring in the successive generations called as variation .it is the difference in the characters among the individuals of a species. The lowest part of our ear is called as earlobes. So the free earlobe and attached earlobe are the two variations found in human population. Types of variation
Somatic or somatogenic variation: - These variations occurred in an individual during life time or lost with death. These variations can’t become genetic so called as temporary variation. Causes of somatic variations
Environmental factors: - those factor which are of environment or climate are responsible for variations. They are light, Temperature, nutrition, air, water or intensity of heat.
Use or disuse of organ or body part:- When a person uses its organs more than the normal, Causes more stress in that organ then it develops more or if the organ uses less than the normal its growth become weak e.g. exercise
Conscious effect: - these are the factor created by the organism for its own betterment called conscious effects E.g. Cutting of horns, Shaving, bear, Nose or ear surgery, Preaching nose, Growing bearded. All these changes are called phenotypic variations.
Germinal, genetic or blastogenic variation: - Those variations which are inherited through genes or passes in generation thus become permanent called as germinal variation.
Continuous Variation:- that variation which passes in nearest generation during segregation of chromosomes or crossing over .These changes made the organism more adopted.E.g. Colour, Size, Weight or formation of more part of our body.
Discontinuous variation: - These variations occurred suddenly in genes than passes into generation .it includes genetic diseases ,genetic mutation ,These are caused by effect of chemical rays .disease like cancer is also discontinuous variations.
Importance of variation: - Traits (or characteristics) of an organism which is caused by a change in its genes (or DNA) is called as inherited trait.
A trait ( or characteristics) of an organism which is ‘not inherited’ but develops in response to the environment is called an acquired trait.The acquired traits of organism cannot be passes on to their future generations. Only those traits can be transmitted to future generations in which changes have occurred in the genes (or DNA) present in the reproductive cells (or gametes) of parent organism.
It gives new characters or traits.
2) It moves the organism more adopted to environment.
3) These variation leads in the evolution of life.
4.) It causes various different species of organism.
5) It makes the individual more adopted to struggle or competition.
Accumulation of variations: - The reproduction of organisms produces variations. The variations produced in organisms during successive generations get accumulated in the organisms. The significance of a variation shows up only if it continues to be inherited by the offspring for several generations. The great advantage of variation to a species is that it increases the chance of its survival in a changing environment. For example, the accumulation of ‘heat resistant’ variation (or trait) in some bacteria will ensure its survival even when the temperature in its environment rises too much due to heat wave or some other reasons. On the other hand, the bacteria which did not have this variation to withstandheat would not survive under thesecircumstances and die.
Types of Chromosome
Metacentric – These chromosomes having centromere at exactly in central place.
Sub metacentric: - These chromosomes in which the centromere shifted in just away from the central position (40-60).
Areocentric :- in this chromosomes the centromere is present very jar from the centre but not at end(15-85)
Telocentric: - That chromosomes in which the centromere is present at one end.
Diploid and Haploid cell:-
Diploid cell: - Those cell whose nuclear contains full number of chromosomes (Paired or 2N) .These cells are somatic cell or zygote ,It can divide according to mitosis.
Haploid cell: - That cell which contains half the number or chromosomes that is only one pair of chromosomes called as N-structure .They are reproductive cell only egg or sperms. They produced by mitosis.
Karotype:- It is a characteristic of an organism of a particular species, Showing the actual chromosomes structure during metaphase ,these chromosomes help to determine genetic deformities if occurred .Banding technique means staining or colouring a particular chromosomes with a particular dye. This technique is done to observe chromosomes very clearly to diagnose the genetic deformation.
Down syndrome: it is a genetic disorder when a nucleus contains one 21st chromosomes extra or less than the normal .If in male the 21st chromosomes false to separate than the sperm contain 24 chromosomes instead of 23 .as it fuses with the normal egg than the resulting chromosomes becomes 47.Than it is called as Down syndrome.
In other case the other sperm lacks of 21st chromosomes by which the resulting zygote has 45 chromosomes also called as down syndrome .In both cases the child has severe mentally retardation flattened nose, dejected ears, widely separated eyes, short and broad neck ,protruding tongue., small or subby hands and feet.
Q .What are genes ?
- Gene is the unit of inheritance and genetic. A chromosome has many segments; each one is called as gene. In one chromosome about 30,000-40,000 genes are present (for human body).DNA (Double helical structure protein)
DNA is a genetic material present in genes of each organism .it has a double helical structure protein (Double,Helix,Spiral)Each strand is called as nucleotide..DNA is ladder like structurewhose horizontal connection is considered as bases `while the vertical connection is considered as pentose sugar with phosphate group .One DNA has two type of nitrogen base one is called as purines (adenine or guanine) &the other is called as pyrimidines (thymine or cytosine.) .Both purines pr pyridines have double and triple bond respectively between them whilethe other end has pentose sugar. The molecule of pentose sugar is different bases or same bases are connected through phosphate molecule. The structure of DNA was discovered by WATSON, CRICK and WICKMEN in 1953 .During miosis the DNA structure opens prepared complimentary bases attached in order to give double strand as DNA.
what is genetic engineering ?
- it is a technique used in alteration of genetic make up of a particular organism by displacement and addition as new genes .taken from the organism called as genetic engineering By the help of genetic engineering we can produce genetically modified organisms (GMO) they are also called as transgenic organism. The genetic engineering helps us to form disease free insect resident crops or more productive crops or animals.
Sex Chromosomes: - in animals ,the last pair of chromosomes which is responsible for determination of sex in babies is called sex chromosomes. in human body the sex chromosomes is 23rd (XX,X-y).
Determination of sex in humans: -(a)In human female, egg carries only X chromosomes while the human sperm carry’s ‘ Y’ chromosomes. IfX chromosomes containing egg fuses with X containing sperm then the zygote contain ( XX) pair of chromosomes results female body.
(b) When X containing egg fuses with y containing sperm then the zygote contains (xy) pair of chromosomes resulting in male baby
(c) When due to malfunctioning of meiosis the egg or sperm contain more X or Y chromosomes then the zygote contains more number of X or Y chromosomes (Sex chromosomes) it is called kleinefelttr’s syndrome.
SEX determination in ANIMAL’S:- In some animals, sex determination is also controlled by the environmental factors. The incubation period or temperature results in the determination of sex in some animals like reptiles. Due to high temperature little faster incubation results in the formation of male or opposite the low temperature slow in incubation results in the female .E.g. –in turtles high incubation temperature creates female progeny but in lizards the high incubation temperature creates male progeny.
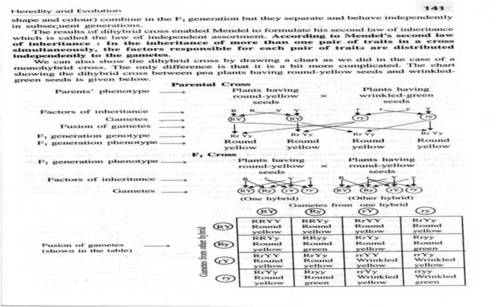
Mendel select Pea plant for his experiment:-The pea plant has set of contrasting characteristics like tall and dwarf plants, white, yellow, violet and pink flowers, round and wrinkle seeds and yellow and white seeds. These plants have less life span so regrown again and again to check the accumulated variations. Pea plant also grown in any type of conditions.
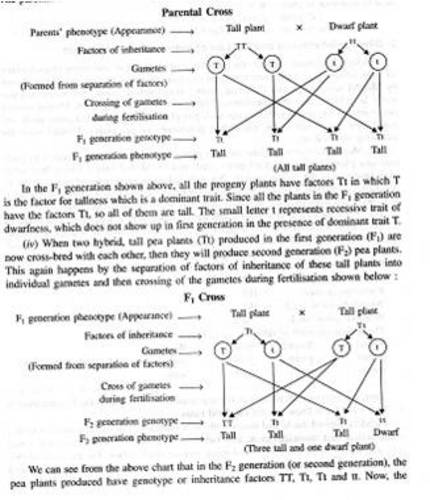
Principle of inheritance: - when two organism of same type with same characters are interbreed than we get exactly same character again e.g. if cross breed .tall type of pea plant with small type of pea plant we get true tall plant ,is called as true breed or pure breeding.
If we interbreed two different organism having characters than after 1st breed we get the offspring in three ratios, Dominance one receive 1st time in second generation it gives 9:3:3:1.
Law of dominancy: - out of pair of contrasting characters only one is able to express itself phenotypically (outer appearance while) the other remains hidden .The one which is expressed is dominant and the other is recessive.
Law of segregation:-Two members of a pair of factors separate during the formation of gametes .They do not blend with each other but segregate out in to different gametes. It is also called as law of purity of gametes.
Insert Another Sub Header Here
Q-Difference between RNA and DNA
Differences Of RNA
It is a type of Ribose sugar
It has a single helix structure or strand.
It has 4 bases which are independent on bonds but instead of thyamine it has uracil
It is found outside or inside the nucleus according to formative stages
DNA was discovered by Wikin
E.g. Blue green algae, retrovirus(HIV)
Difference Of DNA
1) it is deoxy ribose sugar
2) it has a double helix structure or strand
3) It has four bases join together with weak by
hydrogen bond and it has thymine
4) it is present only inside the nuclear membrane.
5) The structure of DNA was given by J.D.Watson and
cricks
6) E.g. Protozoa, Man ,Cat
Q-Difference between Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
Autosomes
They are some type in males or females
They are of 3 types meta, Sub, acru, type.
They are of more in no of pairs
During metosis autosomes or a sex chromosomes do not separate
Sex chromosomes
They are of different type in males or females(Y,X)
It is of Telocentric type
They are only one different only in pair only in meiosis only, sexchromosomes separate.
(1) Organic Evolution It is the sequences of gradual changes which take place in the primitive organisms over millions of year to give new, more specified organisms & species created. It is two type
Progressive Evolution- In this evolution simpler organism evolved in more complex organism.
Retrogressive Evolution:- That evolution in which formed complex .Organism Developed into more simpler organism.
Evidence of evolution:-
By some character ,Some development stages or by the help of developed Baby we can estimate about evolution
Fossils – These are remains or impressions of dead animals And plants which lived in Remote .Past or help us to relay the evolutionary changes .Archaeopteryx looks like a bird but retains some features of reptiles ,It has teeth in mouth while beaks of birds has no teeth.
To determine the age of fossil we use radiocarbon dating method or C14 method. Secondly the layers of the earth and formation of these layers in sequence gives the age.
There are various kinds of fossils. Some of the important fossils which have been studied of those of ammonite, trilobite and dinosaur. The estimation of the age of ammonite fossil have told us that they are about 180 millions years old.
Homologous Organ: Those having some structure and origin but they perform different function in different organism Eg. Flippers of seal ,Wings of bat ,Birds, four limbs of horse, or man have same structure but they perform different function
Analogous Organs:- Those having different structure or origin but they perform same function for organism called as analogous organ E.g –Wings of birds or an insect ,Fins of fish.
Vestigial Organs:- Those organ having different structure or function but they becomes functionless in some organism .But they have imp function in their ancestor or other organism E.g. Canine teeth in human body and bog third eyelids of man amphibian of reptile very from appendices,ear muscles.
Embryology:- It is the study of development of an embryo of an animal from a zygote. The study of embryo shows the biogenetic law.
Biogenetic law :- According to carllinnaaeus,The evolution is slow on going process of formation of more species from persisting according to this law on togens recapitulate phylogency of any organism completes all the evolutionarily history and changes of past.
The theory of organic Evolution
According to carllinnaeaus, the evolution is the slow on going process of formation of move species from pre-existing ones.
Lamarck’s Theory:-
The effect of environment:-Due to changes in environmental condition. Some outer variations are caused which may become inherited.
Use or disuse of body parts:- it causes effort on various organs to develop more ,strong more usable or other organ become small and small, Finally disappear.
Favorable Variation: Some variation caused by adoption to changing environment finally becomes genetic .E.g- Formation of whale.
Darwin’s Theory:-According to Charles Robert Darwin in the book “.The Origin of species”. The theory of evolution proposed by Darwin is known as” The theory of natural selection .it is also called “Darwinism”
With in any population, there is natural selection which favours some variation then others.
Due to maintaining a species the particular organism produce more and more of their off springs .Ex-most preyed animals reproduce maximum.
Struggle for existence :it refers for inter of intre species competation
Survival of fittest:-The organism which is more adoptive to environment or which can cope the variatic conditions, survive or maintain itself.
Progeny from generation: - The organism contains some memories of future life even before the time of birth.
Variation get accurately over a long period of time had to origin of anew species.
Speciation:-A species is a population of organisms consisting of similar individuals which can breed together and produce fertile offspring. Species can be of plants or of animals .wheat, paddy, sunflower, lotus, mango, neem, humans, tiger, dog and cat, etc., are all examples of various types of species. The human beings who look so different from each other in terms of size, colour and looks are said to belong to the same species (Homosapiens) because they can interbreed to produce fertile offspring's (sons and daughters). The process by which new species develop from the existing species is known as speciation. In simple words, the formation of new species is called speciation. We will now explain how new species are formed from the existing species of various populations
the important factors which could lead to the rise (or formation) of a new species are the following :i) Geographical isolation of a population caused by various types of barriers (such 1smountain ranges, rivers and sea). The geographical isolation leads to reproductive isolation reduce to which there is no flow of genes between separated groups of population. (il) Genetic drift caused by drastic changes in the frequencies of particular genes try chance alone.(iii) Variations caused in individuals due to natural selection. It should be noted that geographical isolation is the major factor in the speciation of the sexually reproducing animals because it interrupts the flow of genes between their isolated populations through the gametes. The geographical isolation, however, cannot be a major factor in the speciation of a self-pollinating plant species because it does not have look to other plants for its process of reproduction to be carried out. (Geographical Isolation also cannot be a major factor in the speciation of an asexually reproducing organism because it does not require any other organism to carryout reproduction.
Evolution of Eyes:-The complex body organs of animals such as eyes have been created in stages over many generations. In Planaria rudimentary eyes are formed. The eyes of flatworm are very simple that are actually just’ eyes spots’ which can detect light. Even these rudimentary eyes provide a survival advantage to flatworm. Starting from basic design, more and more complex eyes were evolved in various organism.
Evolution of Feather:- Sometimes an evolutionary change produced in an organism for one purpose later on becomes more useful for an entirely different function. For example, birds evolved feathers as ameans of providing insulation to their bodies in cold weather but later on these feathers became more useful for the purpose of flying. Even some dinosaurs had feathers though they could not fly by using these feathers. Birds, however, adapted feathers for flying. The presence of feather on birds tells us that the birds are very closely related to reptiles because dinosaurs (which had feathers) were reptiles.
Evolution by Artificial Selection :- In the evidence for evolution we have studied that very dissimilar looking structures can evolve from a common ancestral body design. The wild cabbage plant is a good example to prove that entirely different looking organisms can evolve from the same organism by the process of evolution. The only difference is that here we are using artificial selection for evolution in place of natural selection. The farmer have been cultivating wild cabbage as a food plant for over two thousand years and have produced (or evolved) entirely different looking vegetables like cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kohlrabi and kale from it by artificial selection.
(a) Some farmers wanted to have very short distances between the leaves of wild cabbage and produced the common variety of ‘cabbage’.
(b)When farmer opted for arrested flower development of wild cabbage plant, it lead to the production of other variety of cabbage called as ‘broccoli’.
(c) Some farmers went in for sterile parts of wild cabbage and developed another variety of cabbage called ‘cauliflower’.
(d) When farmers opted for the swollen parts of wild cabbage, it led to the evolution of a yet another variety of cabbage called ‘kohirabi’.
(e) And finally, the farmers wanted to grow large leaves of wild cabbage and ended up producing a leafy vegetable called ‘kale’ which is also a variety of wild cabbage.
(f) Wild cabbage is the ancestor and cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kohlrabi and kale are all its varities which have been obtained by evolution ‘induced artificially by the farmers.
Evolution Should Not be Equated with Progress:- There is no real progress in the concept of evolution. Evolution is just the production of diversity of life forms and shaping of this diversity by the environmental selection. The only progress in evolution appears to be that more and more complex body designs of organism have emerged over the ages. When the new species is formed, it is not necessary that the old species will disappear (or get eliminated) from earth. It will all depend on the environment. The newly formed species are in any way better than the older ones. It is simply that genetic drift and natural selection processes have combined to form a population having different body design which cannot interbreed with the older population. It is a common belief that chimpanzees are the ancestors of human beings have evolved from chimpanzees. Actually, both chimpanzees and human beings had a common ancestor’s long time ago. The two offspring of that ancestor evolved in their own separate ways to form the modern day chimpanzees and human beings.
Human Evolution:- Human Evolution has been studied by using the various tools of tracing evolutionary relationships like excavating (digging earth), carbon-dating, studying fossils and determing DNA sequences. There is so much diversity of human body and features on the earth for a long time people used to different ‘races’ of human beings. The human races were even identified on the basis of their skin color and named as white, black, yellow or brown. That so called human races have not evolved differently. In fact there is no biological basics of dividing human beings into different ‘races’. All humans beings (whether, white, black, yellow or brown) are a single species (called Homo sapiens).
Origin of life on earth:- A British scientist J.B.S. Haldane suggested in 1929 that life must have developed from the simple inorganic molecules (such as methane, ammonia, hydrogen sulphide, etc.) which were present on the earth soon after it was formed. He said that the conditions on earth that time (including frequent lighting) could have converted simple inorganic molecules into organic molecules which were necessary for life. These complex organic molecules must have joined together to form first primitive living organisms. Haldane also suggested from theoretical considerations that for life (or living organisms) originated in a sea water,
The theory of origin of life on the earth proposed by Haldane was confirmed by experiments conducted by Stanely L.Miller and Harold C. Urey in 1953. They assembled an apparatus to create an early earth atmosphere which was supposed to consist of gases like methane, ammonia and hydrogen sulphide, etc., (but no oxygen), over water. This was maintained at a temperature just below 100o C and electric sparks were then passed through the mixture of gases (to stimulate lighting) for about one week. At the end of one week, it was found that about carbon including ‘amino acids’ which make up protein molecules found in living organisms.